Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality in Missouri State: Contaminants, Issues, and Water Filtration Solutions
by Ryan Moreau / updated February 10th, 2025
Missouri, known as the “Show-Me State,” is rich in water resources, from the mighty Mississippi and Missouri Rivers to its numerous lakes and aquifers. However, this abundance comes with challenges. Agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and aging infrastructure contribute to water quality issues affecting both urban and rural communities. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the common contaminants in Missouri’s water, regional challenges, and effective filtration solutions. Start by using our Water Quality Tool to get a customized analysis of your local water conditions.

Overview of Missouri’s Water Sources
Missouri’s water supply is diverse, encompassing vast river systems, lakes, and groundwater aquifers. Key sources include:
- Missouri River: One of the longest rivers in North America, it provides water for agriculture, industry, and some municipal uses.
- Mississippi River: Forming Missouri’s eastern border, it is a major source for transportation and industrial activities.
- Ozark Aquifer: A significant groundwater source supplying rural communities and small towns in southern Missouri.
- Reservoirs and Lakes: Bodies such as Lake of the Ozarks and Table Rock Lake serve both recreational and water supply purposes.
altWith such varied sources, maintaining water quality requires coordinated efforts between state agencies, local governments, and community stakeholders.
Common Water Quality Contaminants in Missouri
Missouri’s water faces contamination from agricultural activities, industrial operations, and natural geological factors. To better understand what might affect your area, start with our Water Quality Tool and review these common issues:
1. Nitrates
Agricultural runoff is a significant source of nitrates in Missouri’s water supplies. Excessive use of fertilizers leads to nitrates leaching into groundwater and surface water, posing health risks especially to infants and pregnant women. Elevated nitrate levels can lead to methemoglobinemia or “blue baby syndrome.”
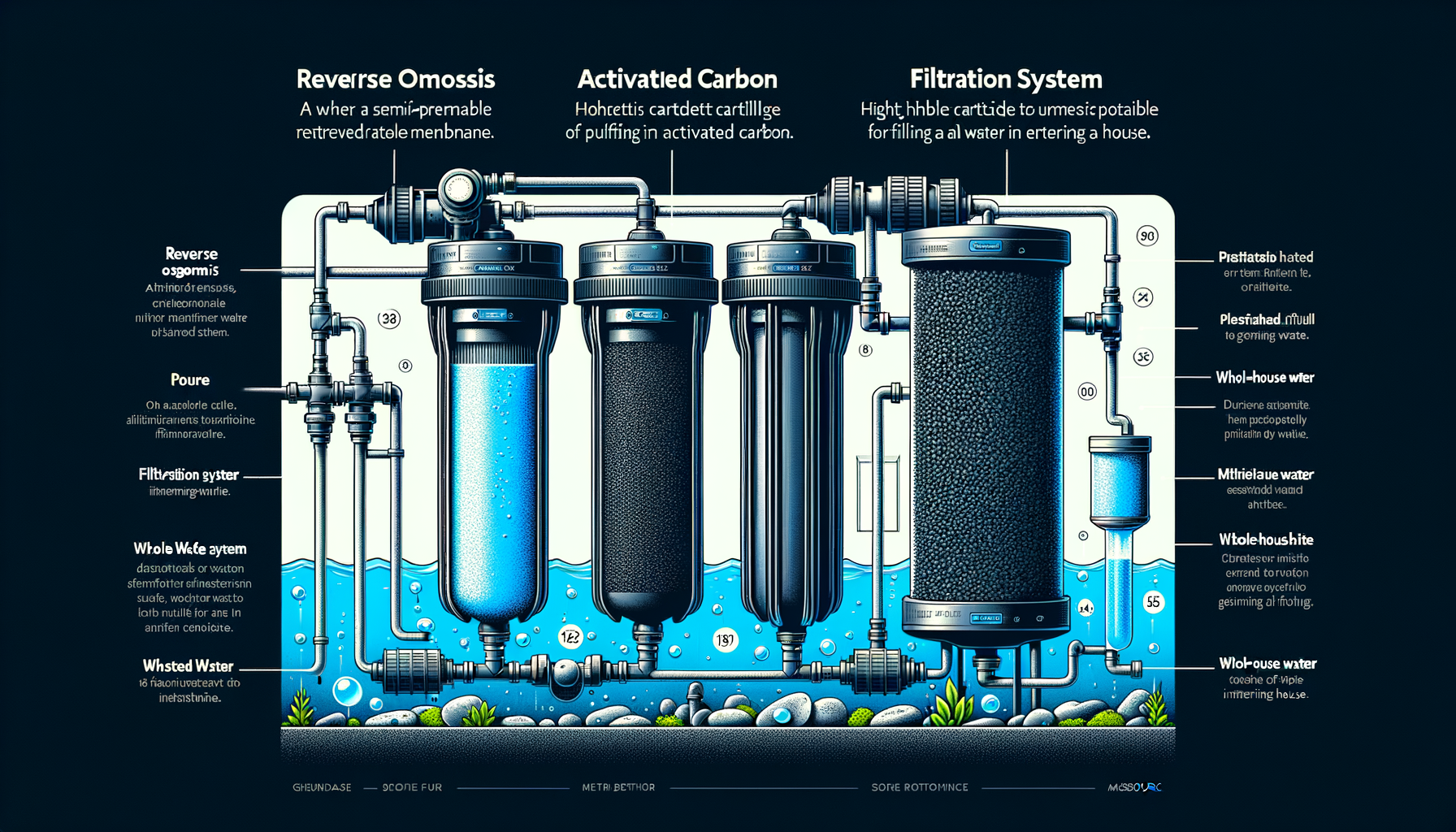
Water Filtration Options for Nitrates: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
2. Lead and Copper
Aging water infrastructure in some Missouri cities, such as St. Louis and Kansas City, can result in elevated levels of lead and copper in drinking water due to pipe corrosion. Lead exposure is particularly harmful to children, affecting neurological development.
Water Filtration Options for Lead and Copper: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
3. Atrazine
Atrazine is a commonly used herbicide in the Midwest, including Missouri, to control weeds in corn and sorghum fields. It can runoff into water supplies, and long-term exposure is linked to endocrine disruption and reproductive issues.
Water Filtration Options for Atrazine: Activated Carbon Water Filters, Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
4. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Industrial activities, particularly in urban areas and near manufacturing plants, can lead to VOCs like benzene and toluene contaminating water sources. These compounds are associated with various health risks, including cancer and organ damage.
Water Filtration Options for VOCs: Activated Carbon Water Filters
5. Bacteria and Microorganisms
Private wells, especially in rural areas, may be susceptible to contamination by bacteria such as E. coli and coliforms due to septic system leakage or agricultural runoff. These microorganisms can cause gastrointestinal illnesses.
Water Filtration Options for Bacteria: Ultraviolet (UV) Water Filters, Reverse Osmosis Systems with UV disinfection
6. Radionuclides (Radium and Uranium)
Certain regions in Missouri, particularly those with sedimentary rock formations, may have natural deposits of radioactive elements like radium and uranium in groundwater. Long-term exposure can increase the risk of cancer.
Water Filtration Options for Radionuclides: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, ion exchange systems
7. Iron and Manganese
High levels of iron and manganese are common in Missouri’s groundwater, causing staining on plumbing fixtures and laundry, as well as affecting water taste and appearance.
Water Filtration Options for Iron and Manganese: Oxidation filtration systems, Whole House Water Filters designed for iron removal
8. Sulfates
Sulfate minerals are present in Missouri’s geology, sometimes leading to high sulfate levels in groundwater. Elevated sulfates can cause a laxative effect and contribute to scale buildup in plumbing.
Water Filtration Options for Sulfates: Reverse Osmosis Systems, distillation units
Regional Water Quality Challenges in Missouri
Missouri’s diverse regions face unique water quality issues due to variations in industrial activity, agricultural practices, and geological formations. Key challenges include:
1. Northwest Missouri: Agricultural Runoff
The intensive farming activities in this region contribute to elevated nitrate and pesticide levels in water sources. Fertilizer and chemical runoff from croplands affect both surface water and groundwater quality.
2. Southeast Missouri: Lead Mining Legacy
The “Old Lead Belt” in southeast Missouri has a history of extensive lead mining, leaving behind contaminated soils and water sources. Lead and other heavy metals can leach into groundwater, posing long-term health risks (Missouri DNR – Superfund Sites).
3. Urban Areas: Aging Infrastructure
Cities like St. Louis and Kansas City grapple with aging water distribution systems. Corrosion of old pipes can lead to lead and copper contamination, necessitating infrastructure upgrades.
4. Ozark Plateau: Karst Topography Vulnerability
The Ozark region’s karst landscape, characterized by sinkholes and caves, makes groundwater highly susceptible to contamination from surface activities. Pollutants can rapidly infiltrate aquifers, requiring careful land use management.
General Water Characteristics in Missouri
Understanding the general characteristics of Missouri’s water helps in selecting appropriate treatment solutions:
1. Water Hardness
Water hardness is a common issue across Missouri, with many areas experiencing moderate to hard water due to high levels of calcium and magnesium. Hard water can lead to scale buildup in appliances and reduce the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
For households dealing with hard water, installing a water softener can greatly improve water quality. If you’re unsure whether you need a water softener or which type suits your family’s needs, try our Water Softener Calculator for personalized guidance.
2. Taste and Odor Issues
In some regions, dissolved minerals like iron and manganese can impart a metallic taste or cause an unpleasant odor in the water. Sulfur compounds, resulting in a “rotten egg” smell, may also be present in certain groundwater sources.
- Organoleptic Qualities: Affect the taste, smell, and appearance of water.
- Impacts on Daily Use: Can discourage consumption and affect cooking and beverages.
Activated carbon filters and oxidation filtration systems can help eliminate these taste and odor issues.
3. Turbidity and Sediment
Surface water sources, particularly after heavy rains, can carry increased sediment loads, leading to higher turbidity. Sediments can harbor microorganisms and reduce the effectiveness of disinfection processes.
- Filtration Needs: Sediment filters can protect plumbing and improve water clarity.
- Equipment Protection: Reduces wear and clogging of fixtures and appliances.
Installing sediment pre-filters is advisable for households drawing water from surface sources or shallow wells.
Utilizing the Water Quality Tool for Missouri Residents
To tackle water quality concerns effectively, it’s crucial to understand the specific issues affecting your area. Our Water Quality Tool allows Missouri residents to:
- Input their zip code for a tailored analysis of local water sources
- Access data on common contaminants in public and private water supplies
- Get personalized recommendations for filtration systems based on regional challenges
This tool serves as a starting point for addressing your home’s water quality needs.
Recommended Filtration Solutions for Common Missouri Contaminants
Based on the contaminants prevalent in Missouri’s water sources, the following filtration systems are recommended:
1. Reverse Osmosis Systems
Ideal for removing nitrates, atrazine, lead, and radionuclides, Reverse Osmosis Systems provide comprehensive purification. They are suitable for point-of-use installations like under the kitchen sink.
2. Activated Carbon Filters
Activated Carbon Filters effectively reduce VOCs, pesticides, herbicides, and improve taste and odor by removing chlorine and organic compounds.
3. Water Softeners
For addressing hard water issues, Water Softeners can remove excess calcium and magnesium, preventing scale buildup and extending the lifespan of appliances.
4. UV Disinfection Systems
To eliminate bacteria and other microorganisms in private wells, Ultraviolet (UV) Water Filters can be installed either as standalone units or integrated with other filtration systems.
Local Water Testing Services in Missouri
To accurately identify contaminants in your water, professional testing is essential. We recommend using SimpleLab for comprehensive water quality analysis. Their easy-to-use kits and detailed lab reports empower you to make informed decisions about water treatment solutions.
Additionally, the Missouri Department of Health and Senior Services offers resources and guidance for private well testing (Missouri DHSS – Private Water Supplies).
Case Studies: Addressing Water Quality Issues in Missouri
Real-world examples highlight how water quality challenges in Missouri are being tackled:
1. St. Louis: Infrastructure Improvements
The city has launched initiatives to replace lead service lines and upgrade water treatment facilities. Public awareness campaigns educate residents on the importance of filtering tap water and proper maintenance of home plumbing systems.
2. Rural Communities: Managing Agricultural Runoff
Programs promoting sustainable farming practices and buffer zones along waterways help reduce nitrate and pesticide contamination. Farmers are encouraged to adopt precision agriculture techniques to minimize fertilizer application (Missouri Soil and Water Conservation Program).
3. Southeast Missouri: Remediation of Mining Sites
Efforts are underway to clean up former lead mining areas through soil remediation and water treatment projects. Community outreach ensures residents are informed about potential risks and mitigation strategies (Missouri DNR – Superfund Program).
Call to Action
Missouri’s abundant water resources are vital to its communities, agriculture, and industry. However, diverse contaminants pose challenges that require proactive management. By understanding local water quality issues and implementing effective filtration solutions, you can ensure the safety and quality of your household’s water.
Begin by entering your zip code into our Water Quality Tool for a detailed analysis of your water supply. Explore our filter review articles to find the most suitable system for your needs, and confirm your water’s safety with comprehensive water testing services. Together, we can protect Missouri’s water for current and future generations.