Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality in Alabama: Contaminants, Issues, and Water Filtration Solutions
by Ryan Moreau / updated February 15th, 2025
Alabama is blessed with abundant water resources, from the winding rivers of the Tennessee and Alabama River systems to the coastal waters of the Gulf of Mexico. However, the state faces significant water quality challenges due to agricultural runoff, industrial pollution, and aging infrastructure. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the common contaminants in Alabama’s water, regional water quality challenges, and effective filtration solutions. Start by using our Water Quality Tool to get a customized analysis of your local water conditions.
Overview of Alabama’s Water Sources
Alabama’s water resources are extensive and varied, providing vital support for its ecosystems, agriculture, industry, and communities. Key water sources include:
- Rivers: Major rivers such as the Tennessee, Alabama, Tombigbee, and Coosa Rivers serve as crucial water supplies for municipalities, agriculture, and industry.
- Lakes and Reservoirs: Lakes like Lake Guntersville, Lake Martin, and Logan Martin Lake are important for drinking water, recreation, and hydropower generation.
- Groundwater Aquifers: Many rural communities in Alabama depend on groundwater from aquifers like the Coastal Plain Aquifer System for their drinking water.
- Coastal Waters: The Mobile Bay and Gulf of Mexico are significant not only for their ecological value but also for providing water for various uses in coastal regions.
With such diverse water sources, Alabama faces unique challenges in ensuring water quality across the state. Vigilant monitoring and effective water treatment are essential to maintain the health and safety of these water supplies for all Alabamians.
Common Water Quality Contaminants in Alabama
Alabama’s water sources may contain a range of contaminants stemming from industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, mining activities, and natural geological formations. To better understand what might affect your area, start with our Water Quality Tool and then review these common issues:
1. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAs)
PFAs have been detected in certain areas of Alabama, particularly near former industrial sites and military bases where firefighting foams containing PFAs were used. Chronic exposure to these “forever chemicals” can lead to adverse health effects, including hormonal disruptions and increased risk of certain cancers. For more detailed information, visit the EPA PFAs Tools and our PFAs Contamination Guide.
Water Filtration Options for PFAs: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
2. Nitrates
Agricultural activities in Alabama, particularly in regions with intensive farming, can result in elevated nitrate levels in groundwater. Nitrates are especially dangerous for infants, causing methemoglobinemia or “blue baby syndrome,” which can interfere with the blood’s ability to carry oxygen.
Water Filtration Options for Nitrates: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
3. Arsenic
In certain areas of Alabama, natural deposits of arsenic in the bedrock can leach into groundwater, especially in private wells. Prolonged exposure to arsenic-contaminated water may increase the risk of skin lesions, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
Water Filtration Options for Arsenic: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
4. Chlorine and Disinfection Byproducts
Many of Alabama’s municipal water systems use chlorine for disinfection to kill harmful microorganisms. However, this process can lead to the formation of disinfection byproducts such as trihalomethanes (THMs) and haloacetic acids (HAAs), which have been associated with long-term health risks, including cancer and reproductive issues.
Water Filtration Options for Chlorine and Disinfection Byproducts: Activated Carbon Water Filters, Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
5. Heavy Metals (Lead and Copper)
Aging water infrastructure in some Alabama communities, particularly in older urban areas, can result in lead and copper leaching into the water supply. Corrosion of pipes and plumbing fixtures is the primary source of these contaminants, which can have severe health impacts on children, including developmental delays and neurological damage.
Water Filtration Options for Heavy Metals: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
6. Microbial Contaminants
In rural areas of Alabama, private wells may be susceptible to microbial contamination due to surface runoff, flooding, or improper well maintenance. Bacteria such as E. coli and viruses can cause gastrointestinal illnesses and other infections when ingested.
Water Filtration Options for Microbial Contaminants: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters with UV disinfection or UV Water Purifiers can effectively neutralize bacteria and viruses.
7. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
In Alabama, VOCs can contaminate water supplies near industrial sites, landfills, or gasoline stations due to spills and improper disposal. Compounds like benzene, toluene, and xylene can have serious health impacts, including damage to the liver, kidneys, and nervous system.
Water Filtration Options for VOCs: Activated Carbon Water Filters
8. Pesticides and Herbicides
Due to Alabama’s significant agricultural activities, runoff containing pesticides and herbicides can enter water bodies and groundwater. Chemicals like atrazine and glyphosate have been detected in some water supplies, with potential risks including endocrine disruption and other health issues.
Water Filtration Options for Pesticides and Herbicides: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
9. Fluoride
While fluoride is added to many municipal water supplies in Alabama to prevent tooth decay, some regions may have naturally occurring high levels of fluoride in groundwater. Excessive fluoride intake over time can lead to dental fluorosis in children and skeletal fluorosis in severe cases.
Water Filtration Options for Fluoride: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
Regional Water Quality Challenges in Alabama
Alabama’s varied geography, ranging from mountainous regions to coastal plains, combined with its industrial and agricultural activities, presents unique regional water quality challenges. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Alabama Department of Environmental Management (ADEM), key challenges include:
1. Industrial Pollution in the Tennessee Valley
The Tennessee Valley region, home to numerous manufacturing plants and industrial facilities, faces challenges in maintaining water quality due to industrial effluents. Contaminants such as heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium), PFAs from manufacturing processes, and VOCs can make their way into the Tennessee River and its tributaries.
These pollutants can accumulate in fish and other aquatic organisms, posing health risks to communities relying on these resources for food. Efforts by the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) and local environmental agencies focus on monitoring and reducing industrial discharges to protect water quality.
2. Agricultural Runoff in the Black Belt Region
The Black Belt region’s extensive agriculture, including cotton, soybean, and livestock farming, contributes significantly to Alabama’s economy. However, the use of fertilizers and pesticides can result in runoff that contaminates nearby water bodies with nitrates, phosphorus, and chemical residues.
This nutrient loading can lead to algal blooms in lakes and rivers, depleting oxygen levels and harming aquatic life—a phenomenon known as eutrophication. Communities in the region must balance agricultural productivity with sustainable practices to protect their water resources.
3. Mining Activities in Central Alabama
Coal and metal mining in Central Alabama have historically affected water quality through acid mine drainage, which occurs when sulfide minerals in exposed rock surfaces react with water and oxygen to produce sulfuric acid. This acid can leach heavy metals into waterways, harming aquatic ecosystems and potentially contaminating drinking water sources.
Regulations and remediation efforts aim to mitigate these impacts, but legacy pollution remains a concern. Monitoring and treatment of mine-affected waters are essential to protect both environmental and public health.
4. Coastal Areas: Saltwater Intrusion
Overutilization of groundwater in Alabama’s coastal communities can lead to a decrease in freshwater pressure, allowing saltwater from the Gulf of Mexico to move inland into aquifers—a process known as saltwater intrusion. This can render drinking water wells saline and unfit for consumption without treatment.
Saltwater intrusion not only affects drinking water but also agricultural soils and ecosystems. Water management strategies, including controlled groundwater extraction and the use of alternative water sources, are being implemented to address this challenge.
General Water Characteristics in Alabama
Apart from the specific contaminants, Alabama’s diverse geology and hydrology contribute to unique water characteristics across the state. Recognizing these traits is crucial in choosing appropriate water treatment solutions:
1. Water Hardness
Alabama’s water hardness can vary significantly depending on the source. In many areas, especially those relying on groundwater from limestone aquifers, water tends to be hard due to high concentrations of calcium and magnesium minerals. Hard water can lead to scale buildup in plumbing fixtures, reduce the efficiency of water heaters, and make it more difficult to form soapsuds.
Residents experiencing hard water issues may benefit from installing a water softener system. To determine if you need a water softener and which type is appropriate for your household, use our Water Softener Calculator for personalized recommendations.
2. Corrosive Water Conditions
In certain areas of Alabama, water sourced from shallow wells or surface water may be slightly acidic, leading to corrosive conditions. Acidic water (low pH) can corrode metal plumbing, causing leaching of metals like lead and copper into the drinking water.
- Low pH Levels: Acidic groundwater can result from the natural dissolution of carbon dioxide or from acid rain infiltrating into the aquifer.
- Risk to Older Homes: Homes with older plumbing systems are especially vulnerable to corrosion-related issues due to outdated materials that may not be corrosion-resistant.
Installing an acid neutralizer system can raise the pH of your water, reducing its corrosivity and protecting your plumbing and health.
3. Impact of Regional Geology
Alabama’s geology, characterized by a mix of sedimentary rock formations like limestone, sandstone, and shale, significantly influences water quality. The dissolution of minerals from these rocks can affect the chemical composition of groundwater.
- Limestone Regions: Areas underlain by limestone, such as the Tennessee Valley and parts of the Black Belt, often have hard water due to high calcium and magnesium levels.
- Iron and Manganese: In some regions, natural deposits can lead to elevated levels of iron and manganese in water, which can cause staining and affect taste.
Using whole house water filtration systems can address these naturally occurring variations in water composition, ensuring consistent water quality for your household needs.
Utilizing the Water Quality Tool for Alabama Residents
Understanding your local water quality is essential for ensuring safe drinking water. Our Water Quality Tool enables Alabama residents to:
- Enter their zip code for a detailed analysis of local water sources
- View data on common contaminants in public and private water supplies
- Receive personalized recommendations for filtration systems based on your water quality challenges
Recommended Filtration Solutions for Common Alabama Contaminants
Based on the prevalent contaminants identified in Alabama’s water sources, the following filtration systems are highly recommended:
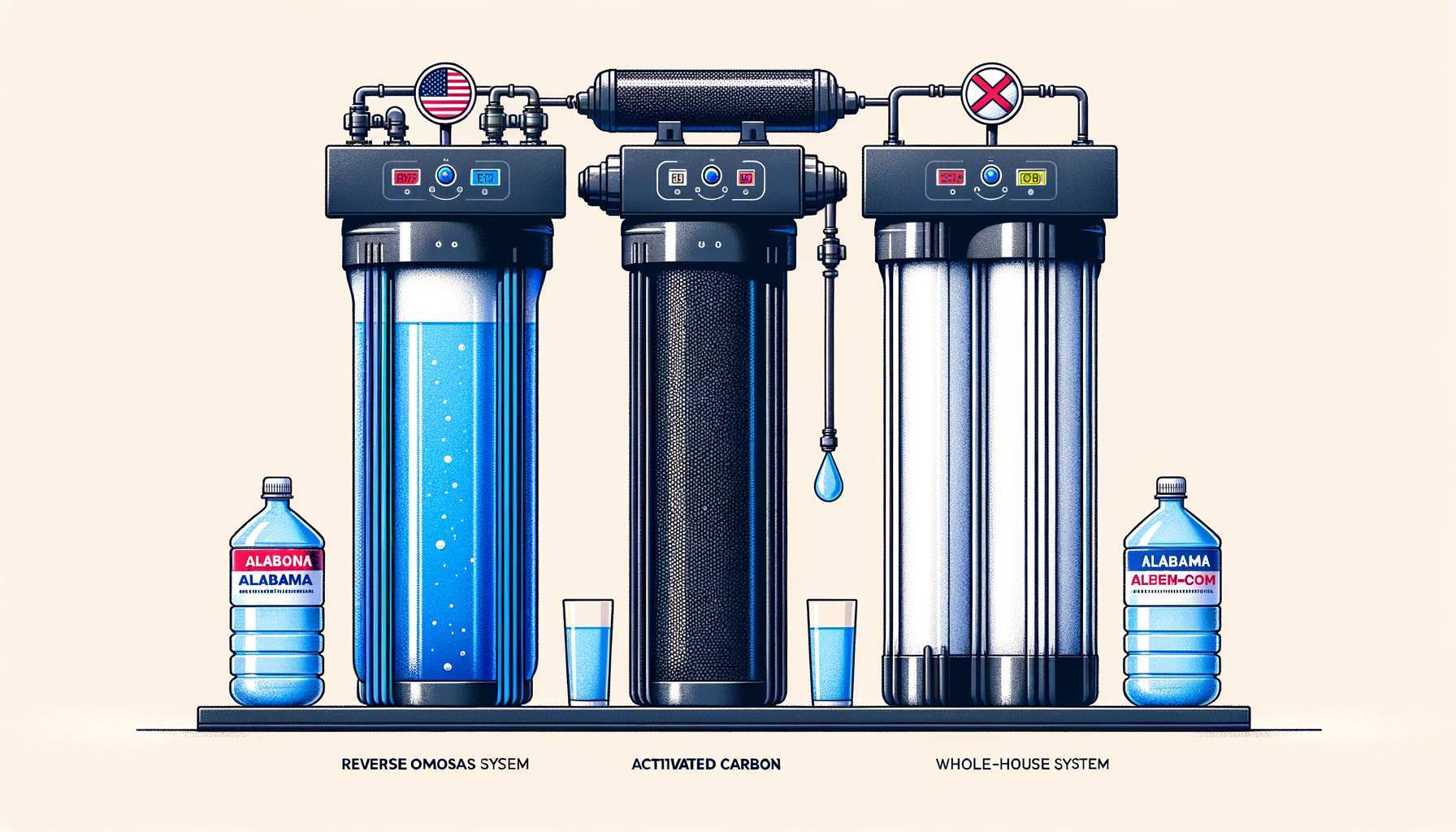
1. Activated Carbon Filters
Activated Carbon Filters effectively remove chlorine, VOCs, and some PFAs while improving taste and odor. They are ideal for municipal water supplies that undergo chlorination.
2. Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse Osmosis Systems offer broad-spectrum removal of nitrates, arsenic, heavy metals, and other contaminants. These systems are versatile for both under-sink and whole-house installations.
3. Whole House Water Filters
Whole House Water Filters provide comprehensive treatment, addressing issues like water hardness, corrosion, and mineral buildup throughout your home.
Local Water Testing Services in Alabama
Accurate water testing is essential to pinpoint the contaminants in your water supply. We recommend using SimpleLab for comprehensive water quality analysis. Their user-friendly kits and detailed lab reports empower you to make informed decisions about your water filtration system.
Case Studies: Addressing Water Quality Issues in Alabama
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how various water quality challenges in Alabama are being addressed:
1. Birmingham: Combating Industrial Pollution
Birmingham, historically known as an industrial hub, has faced challenges with industrial pollutants entering waterways. Initiatives to monitor and reduce discharges, along with community efforts to restore local streams, have helped improve water quality.
Collaborative projects between industries, government agencies, and environmental groups aim to implement cleaner technologies and stricter waste management practices to safeguard water resources.
2. Rural Communities: Addressing Nitrate Contamination
In agricultural regions, community programs promoting best management practices (BMPs) have reduced nitrate runoff into water supplies. Installation of buffer zones and nutrient management plans have been effective in mitigating contamination.
Education and outreach efforts help farmers adopt sustainable practices that protect both their livelihoods and the environment, ensuring safer drinking water for surrounding communities.
3. Mobile County: Managing Saltwater Intrusion
In response to saltwater intrusion threats, Mobile County has implemented groundwater management strategies, including controlled pumping and the development of alternative freshwater sources, to protect aquifers from salinization.
Investments in infrastructure, like desalination plants and water recycling facilities, are being explored to diversify water supply options and reduce pressure on existing freshwater resources.
Call to Action
Alabama’s abundant and diverse water resources require proactive management to ensure their sustainability and safety. Understanding local water quality challenges is the first step in protecting your family’s health.
Start by entering your zip code into our Water Quality Tool for a detailed analysis of your water supply. Then, explore our filter review articles to find the most effective system for your needs. Finally, confirm your water’s safety with comprehensive water testing services to ensure you have the clean, safe water your home deserves.