Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality in Alaska: Contaminants, Issues, and Water Filtration Solutions
by Ryan Moreau / updated February 19th, 2025
Alaska is renowned for its vast and pristine water resources—from the icy glaciers and crystal-clear lakes to the mighty Yukon River. Despite this abundance, the state faces complex water quality challenges due to natural geological formations, industrial activities, and the unique difficulties of supplying clean water to remote communities. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the common contaminants in Alaska’s water, regional water quality challenges, and effective filtration solutions. Start by using our Water Quality Tool to get a customized analysis of your local water conditions.
Overview of Alaska’s Water Sources
Alaska’s water supply is as vast and diverse as the state itself. Key sources include:
- Glacial Meltwater: Glaciers cover a significant portion of Alaska, and their meltwater feeds rivers and streams across the state.
- Rivers: Major rivers like the Yukon, Kuskokwim, and Copper River are vital for drinking water, transportation, and subsistence fishing.
- Lakes and Wetlands: Alaska is home to numerous lakes, including Lake Iliamna, the largest lake in the state, which provide water for communities and ecosystems.
- Groundwater Aquifers: Many rural communities rely on shallow groundwater wells, which can be susceptible to contamination from natural and human-made sources.
Maintaining water quality across these extensive and often remote sources requires vigilant monitoring and innovative treatment solutions tailored to Alaska’s unique environment.
Common Water Quality Contaminants in Alaska
Alaska’s water sources may contain a range of contaminants due to natural geological formations, industrial activities, and inadequate sanitation in remote areas. To better understand what might affect your area, start with our Water Quality Tool and then review these common issues:
1. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAs)
PFAs have been found in parts of Alaska, often linked to military installations, airports, and industrial sites where firefighting foams containing PFAs are used. Chronic exposure can affect thyroid function and immune response. For more detailed information, visit the EPA PFAs Tools and our PFAs Contamination Guide.
Water Filtration Options for PFAs: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
2. Nitrates
Nitrate contamination can occur in areas with septic systems and small-scale agriculture. Elevated nitrate levels pose risks, especially to infants, causing methemoglobinemia, also known as “blue baby syndrome.”
Water Filtration Options for Nitrates: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
3. Arsenic
Natural geological formations in parts of Alaska contribute to arsenic in groundwater. Long-term exposure to arsenic can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular problems and cancer.
Water Filtration Options for Arsenic: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
4. Chlorine and Disinfection Byproducts
Some municipal water systems in Alaska may use chlorination. This can form disinfection byproducts like trihalomethanes (THMs), linked to increased cancer risks over time. However, many remote communities use untreated water, so this issue varies by location.
Water Filtration Options for Chlorine and Disinfection Byproducts: Activated Carbon Water Filters, Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
5. Heavy Metals (Lead and Copper)
Aging infrastructure in some Alaskan towns can lead to concerns over lead and copper contamination. Corrosion in old pipes can release these metals, posing risks particularly for children and pregnant women.
Water Filtration Options for Heavy Metals: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
6. Microbial Contaminants
Many remote villages in Alaska rely on untreated surface water or shallow wells, increasing the risk of microbial contamination from bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Water Filtration Options for Microbial Contaminants: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters with UV disinfection systems can effectively neutralize bacteria and viruses.
7. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
VOCs, such as benzene and toluene, may be present in water sources near oil extraction sites, mining operations, or areas with industrial activities. These compounds are linked to various health risks, including liver and kidney damage.
Water Filtration Options for VOCs: Activated Carbon Water Filters
8. Pesticides and Herbicides
While large-scale agriculture is limited in Alaska, pesticide and herbicide use in certain areas can lead to contamination of water supplies, impacting both human health and aquatic ecosystems.
Water Filtration Options for Pesticides and Herbicides: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
9. Fluoride
Fluoride occurs naturally in some Alaskan water sources. While beneficial in small amounts for dental health, excessive fluoride levels can sometimes occur naturally and may lead to skeletal fluorosis.
Water Filtration Options for Fluoride: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
Regional Water Quality Challenges in Alaska
Alaska’s vast and remote landscapes, along with industrial activities, contribute to various regional water quality challenges. According to the EPA and the Alaska Department of Environmental Conservation (ADEC), key challenges include:
1. Rural Villages: Lack of Sanitation Infrastructure
Many rural communities in Alaska lack adequate sanitation and water treatment infrastructure. Residents may rely on untreated surface water or shallow wells, increasing the risk of bacterial contamination and waterborne diseases. The use of “honey buckets” (portable toilets) and lack of sewage systems can contaminate local water sources.
2. Mining Regions
Areas near mining operations, such as those extracting gold and other minerals, may experience contamination from heavy metals like arsenic and mercury. This can impact both groundwater and surface water quality (EPA – Industrial Wastewater Management).
3. Oil Extraction and Transportation Corridors
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System and other oil extraction activities pose risks of petroleum hydrocarbon contamination. Spills and leaks can affect nearby water sources, impacting both the environment and human health.
General Water Characteristics in Alaska
Beyond specific contaminants, Alaska’s unique geology and climate result in distinct water characteristics. Understanding these traits helps in selecting the right treatment solutions:
1. Cold Water Temperatures
Alaska’s water sources are typically cold year-round. Cold temperatures can affect the efficiency of certain water treatment processes and may influence the selection of filtration technologies. For example, biological treatment processes work slower in cold water.
When choosing a filtration system, consider those designed to operate effectively in lower temperatures.
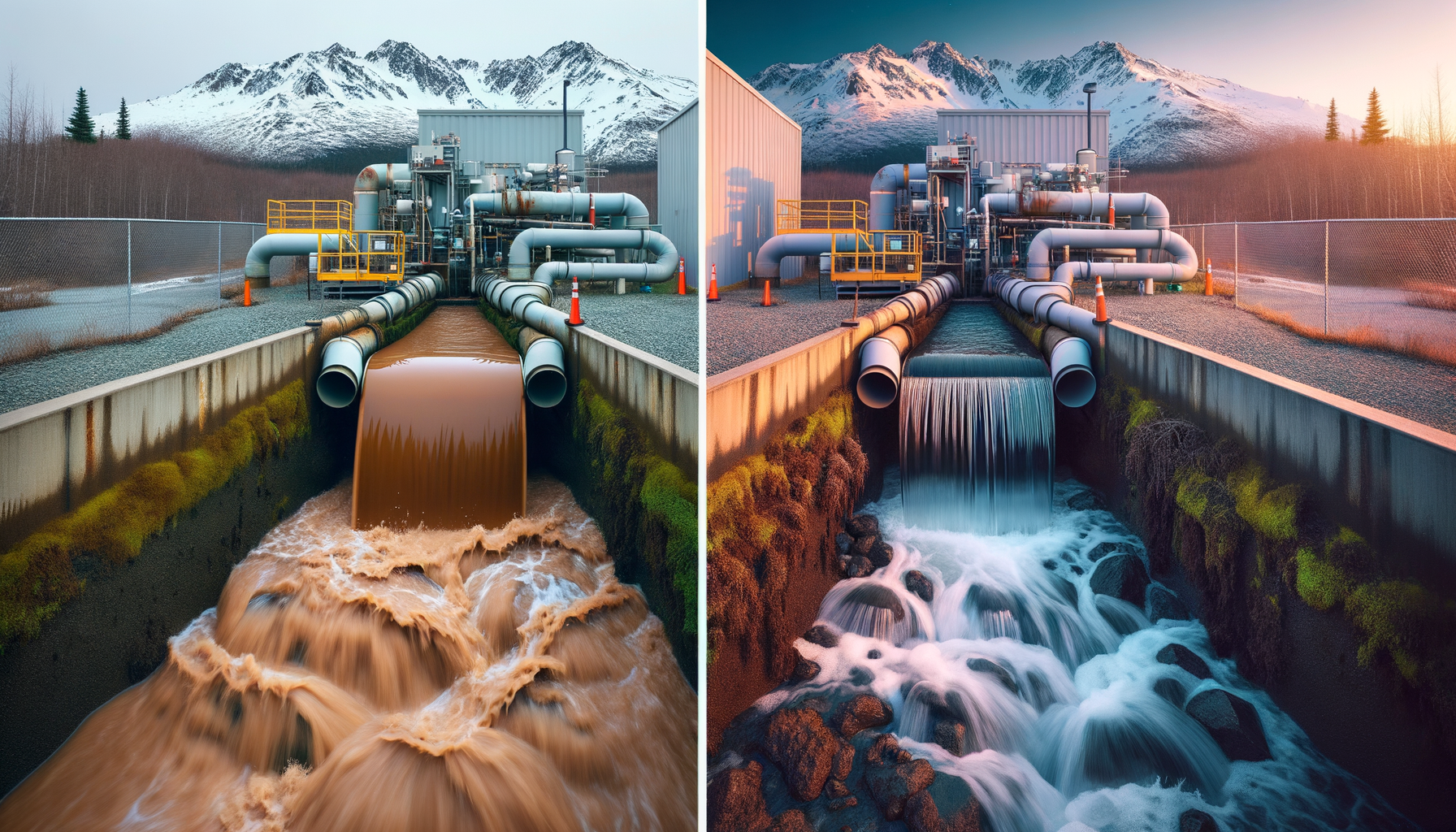
2. High Turbidity from Glacial Silt
Glacial rivers carry fine sediments known as glacial flour, leading to high turbidity levels. This can hinder disinfection processes and cause wear on mechanical parts. Sediment pre-filters are essential to remove particulates before other treatment stages.
Install sediment filters with appropriate micron ratings to handle fine silt typical of glacial waters.
3. Natural Organic Matter
Surface waters in Alaska may contain high levels of natural organic matter (NOM) from decaying vegetation. NOM can react with disinfectants like chlorine to form disinfection byproducts (DBPs), which are harmful over long-term exposure.
Filtration systems combining activated carbon filters with proper pre-treatment can reduce NOM and minimize DBP formation.
Utilizing the Water Quality Tool for Alaska Residents
Understanding your local water quality is essential for ensuring safe drinking water. Our Water Quality Tool enables Alaska residents to:
- Enter their zip code for a detailed analysis of local water sources
- View data on common contaminants in public and private water supplies
- Receive personalized recommendations for filtration systems based on your water quality challenges
Recommended Filtration Solutions for Common Alaska Contaminants
Based on the prevalent contaminants identified in Alaska’s water sources, the following filtration systems are highly recommended:
1. Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse Osmosis Systems offer comprehensive removal of arsenic, nitrates, radionuclides, mercury, and fluoride. These systems are suitable for both under-sink and whole-house installations and are effective even in cold water conditions.
2. Ultraviolet (UV) Water Purifiers
Reverse Osmosis Water Filters with UV disinfection systems can effectively neutralize bacteria and viruses, making them ideal for remote areas relying on untreated surface water or wells susceptible to microbial contamination.
3. Activated Carbon Filters
Activated Carbon Filters effectively remove VOCs, petroleum hydrocarbons, and improve taste and odor. They are essential in areas affected by oil extraction activities.
Local Water Testing Services in Alaska
Accurate water testing is essential to pinpoint the contaminants in your water supply. We recommend using SimpleLab for comprehensive water quality analysis. Their user-friendly kits and detailed lab reports empower you to make informed decisions about your water filtration system.
Case Studies: Addressing Water Quality Issues in Alaska
Real-world examples provide valuable insights into how various water quality challenges in Alaska are being addressed:
1. Village of Tuluksak: Emergency Water Treatment
In 2021, the community of Tuluksak faced a crisis when their only water treatment plant burned down, leaving residents without safe drinking water. Emergency measures, including the provision of water filtration systems and collaboration with government agencies, helped restore access to clean water.
2. Mining Impacts near Fairbanks
Areas near Fairbanks have a history of mining activities, leading to concerns over arsenic and mercury contamination in water sources. Through community advocacy and implementation of advanced water treatment technologies, residents have taken steps to mitigate health risks.
3. City of Anchorage: Addressing Turbidity
The Eklutna Lake, a primary water source for Anchorage, experiences seasonal turbidity due to glacial melt. The municipality has invested in state-of-the-art filtration facilities to ensure consistent water clarity and safety for its residents.
Call to Action
Alaska’s diverse water sources—from remote glaciers and rivers to rural wells—require proactive water quality management. Understanding your local water challenges and implementing effective filtration solutions is essential for safeguarding your household’s health.
Start by entering your zip code into our Water Quality Tool for a detailed analysis of your water supply. Then, explore our filter review articles to find the most effective system for your needs. Finally, confirm your water’s safety with comprehensive water testing services to ensure you have the clean, safe water your home deserves.