Comprehensive Guide to Water Quality in Arizona: Contaminants, Issues, and Water Filtration Solutions
by Ryan Moreau / updated Jan 7th, 2025
Arizona's distinct desert landscape and growing population present unique challenges for water quality and resource management. From the Colorado River providing a significant portion of the state’s water supply to local aquifers supporting rural communities, ensuring safe and clean water is a critical priority. In this comprehensive guide, we examine the most prevalent contaminants in Arizona’s water, discuss regional water quality issues, and outline effective filtration solutions to protect your home’s drinking water. Before exploring our guide, we encourage you to try our Water Quality Tool, which provides a customized water analysis based on your zip code and tailored filtration recommendations.

Overview of Arizona’s Water Sources
Arizona’s water supply is drawn from a variety of sources, each with its own set of challenges and constraints. Major water sources include:
- Colorado River: Providing a substantial portion of Arizona’s surface water through the Central Arizona Project (CAP), which distributes water to Phoenix, Tucson, and surrounding areas.
- Groundwater Aquifers: Significant portions of Arizona rely on groundwater, especially rural communities and agricultural regions. These aquifers can be prone to contaminants like nitrates, arsenic, or PFAs.
- Salt and Verde Rivers: In addition to the Colorado, the Salt and Verde rivers flow into central Arizona, supporting municipalities, irrigation, and recreation.
- Reclaimed Water: Some areas use reclaimed or recycled water for landscaping and agriculture, reducing strain on freshwater sources.
Managing and maintaining water quality in an arid state like Arizona requires careful monitoring, conservation strategies, and advanced treatment technologies to address both current and emerging challenges.
Common Water Quality Contaminants in Arizona
Arizona’s water sources, much like those in other states, are susceptible to a range of contaminants. To understand your specific water quality profile, start by using our Water Quality Tool. Below are the most common contaminants found in Arizona:
1. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAs)
PFAs, often originating from firefighting foams and industrial activities, have been detected near military bases and industrial sites in Arizona. Chronic exposure can affect thyroid function, the immune system, and increase cancer risks. Refer to the EPA PFAs Tools for further data and check out our PFAs Contamination Guide for more information.
Water Filtration Options for PFAs: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
2. Arsenic
Arsenic occurs naturally in Arizona’s groundwater, especially in certain geologic formations across central and southern regions. Long-term exposure can lead to skin lesions, cardiovascular problems, and an elevated cancer risk.
Water Filtration Options for Arsenic: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
3. Nitrates
Agricultural runoff and septic systems commonly raise nitrate levels in groundwater, particularly in rural areas. Elevated nitrates can pose serious health issues for infants, resulting in “blue baby syndrome.”
Water Filtration Options for Nitrates: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
4. Lead and Copper
Like many states, Arizona has pockets of older infrastructure. Corroded pipes can release lead and copper into drinking water, with children and pregnant women most susceptible to neurological and developmental damage.
Water Filtration Options for Lead and Copper: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters, Activated Carbon Water Filters
5. Chromium-6
Some Arizona aquifers contain chromium-6, an industrial byproduct associated with metal plating and manufacturing. Long-term exposure has been linked to various health concerns, including cancer and reproductive issues.
Water Filtration Options for Chromium-6: Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
6. Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs)
Municipal systems often disinfect water with chlorine, which can react with organic material to create disinfection byproducts like trihalomethanes (THMs). These byproducts may contribute to an increased risk of certain cancers.
Water Filtration Options for DBPs: Activated Carbon Water Filters, Reverse Osmosis Water Filters
7. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Arizona’s legacy of industrial and mining activities can contribute VOCs like benzene, toluene, and xylene to groundwater. VOCs can harm the liver and kidneys and raise cancer risks.
Water Filtration Options for VOCs: Activated Carbon Water Filters
Regional Water Quality Challenges in Arizona
Arizona’s arid climate and reliance on limited water sources shape its most critical water quality issues:
1. The Colorado River Basin
The Colorado River supplies a significant share of Arizona’s water via the Central Arizona Project. However, extended drought conditions and interstate allocations place stress on the river’s flow, magnifying pollutant concentrations and raising concerns about future availability.
2. Central Arizona: Growing Urban Demands
Metropolitan areas like Phoenix and Tucson face mounting water demands. Industrial pollutants, aging infrastructure, and groundwater drawdowns can combine to degrade water quality. Monitoring and advanced filtration remain essential for meeting urban needs.
3. Rural Communities and Private Wells
In many rural Arizona regions, private wells are the main drinking water source. Agricultural runoff, septic systems, and naturally occurring minerals like arsenic or radium can compromise well water. Regular testing and targeted filtration are vital to protect public health.
4. Mining Legacy
Historic and active mining operations across Arizona have the potential to introduce heavy metals, such as copper and lead, into local groundwater. Ongoing reclamation efforts and water treatment projects help mitigate these impacts but may not address all legacy pollution sites.
General Water Characteristics in Arizona
Arizona's unique geology and climate conditions significantly affect its general water characteristics. Recognizing these traits helps in choosing optimal water treatment and filtration solutions for your home.
1. High Water Hardness
Hard water is prevalent across Arizona, primarily due to limestone and other mineral-rich deposits in aquifers. This elevated calcium and magnesium content leads to:
- Scale Buildup: Mineral deposits form on fixtures, appliances, and plumbing systems, reducing their lifespan and efficiency.
- Poor Soap Lather: Hard water can diminish the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
To combat water hardness, water softeners are highly recommended. These systems replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium, effectively softening the water. If you’re unsure about the right water softener size or type for your specific hardness levels and household needs, use our Water Softener Calculator to find an optimal solution.
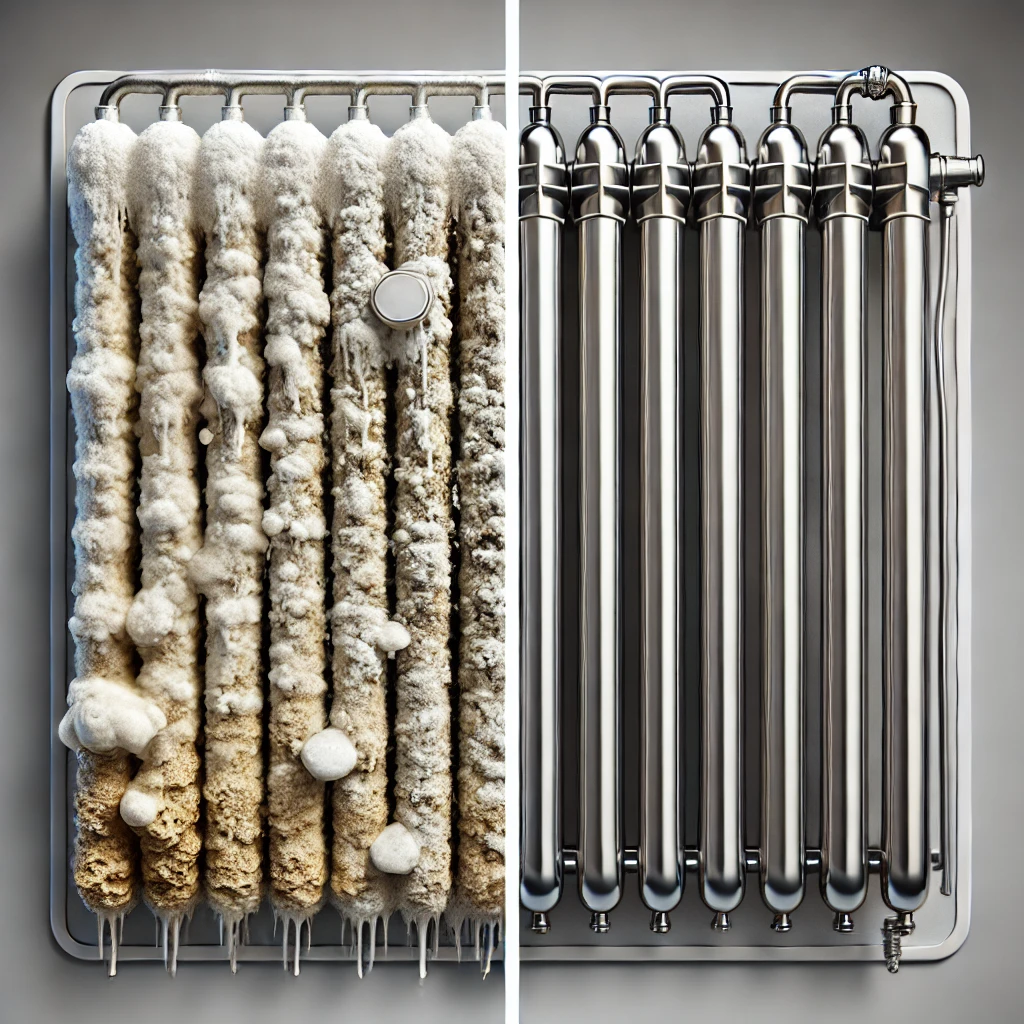

2. Corrosive Conditions in Certain Areas
Some Arizona groundwater sources may be slightly acidic or high in chloride, leading to corrosive water that can leach metals like copper and lead from pipes, especially in older homes.
- Chloride Levels: Elevated chloride content in certain aquifers can corrode plumbing over time.
- Aging Infrastructure: Older urban areas may have pipes that are more vulnerable to corrosive water.
Installing an acid neutralizer can help stabilize pH levels and protect your plumbing from corrosion.
3. Sedimentary Geology and Mineral Content
Arizona’s sedimentary rock layers naturally introduce minerals into groundwater, affecting taste, odor, and overall quality. These minerals may include iron, manganese, or even trace amounts of radium in certain areas.
- Iron and Manganese: Can cause staining and unpleasant taste or smell.
- Trace Radionuclides: Some sedimentary formations may emit low-level radiation into water sources.
Whole house water filtration systems with specialized media (e.g., iron removal filters) or reverse osmosis units can address these issues, improving water quality and palatability.
Utilizing the Water Quality Tool for Arizona Residents
Staying informed about your local water quality is the first step to ensuring clean and safe water in your home. Our Water Quality Tool helps you:
- Identify prevalent contaminants by entering your zip code
- Review pollution data for public water systems and private wells
- Explore recommended filtration options tailored to your area’s specific water issues
This resource simplifies the process of choosing the most effective water treatment solutions for your household.
Recommended Filtration Solutions for Common Arizona Contaminants
Given the range of contaminants found in Arizona, the following solutions are highly recommended:
1. Activated Carbon Filters
Activated carbon effectively removes chlorine, various PFAs, VOCs, and improves water taste. Municipal systems using chlorine disinfection benefit significantly from activated carbon water filters.
2. Reverse Osmosis Systems
Reverse osmosis systems provide broad-spectrum filtration for arsenic, nitrates, lead, copper, chromium-6, and other contaminants common in Arizona. Learn more from our best reverse osmosis water filters article.
3. Whole House Water Filters
For managing scale, corrosion, or elevated iron and manganese, whole house water filters are essential. These systems treat all water entering your home, protecting plumbing and ensuring consistent water quality from every tap.

Local Water Testing Services in Arizona
Identifying the precise contaminants in your water is crucial for effective filtration. We recommend using SimpleLab for comprehensive water quality testing. Their user-friendly kits and lab-based analysis help you make informed decisions tailored to Arizona’s unique conditions.
Case Studies: Addressing Water Quality Issues in Arizona
Real-world scenarios illustrating how water quality challenges are being managed across Arizona:
1. Tucson: Reducing PFAs Levels
Military sites near Tucson have historically contributed PFAs to local groundwater. The city has introduced granular activated carbon (GAC) treatment in wells with high contamination to reduce PFAs concentrations.
2. Yuma: Combating Agricultural Runoff
Known as the "Winter Lettuce Capital," Yuma relies heavily on irrigation from the Colorado River. Increased nitrates from fertilizer runoff have led to pilot programs promoting precision agriculture and advanced filtration systems, effectively lowering nitrate levels in municipal and private wells.
3. Phoenix: Tackling Hard Water and Infrastructure Strains
The Phoenix metropolitan area contends with high water hardness due to groundwater sources and Colorado River supply. Many households have installed water softeners to mitigate scale and corrosion, while municipal authorities focus on infrastructure upgrades to manage demand and maintain quality.
Water contamination poses significant risks to health and the environment. Many factors contribute to the presence of contaminants in water sources, ranging from industrial waste to agricultural runoff.

This image depicts common pathogens and harmful particles in water. Addressing such contamination requires effective filtration systems to ensure safe and clean drinking water for communities.
Call to Action
Arizona’s arid environment and reliance on limited water sources highlight the importance of proactive water quality management. Whether dealing with PFAs near military bases, arsenic in groundwater aquifers, or scale-inducing hardness, understanding your specific water challenges is the first step to ensuring a safe, reliable supply.
Take control of your water quality by entering your zip code into our Water Quality Tool for a detailed analysis of local contaminants. Explore our filter review articles to find the most effective solutions for your household. Finally, test your water through reliable, professional water testing services to confirm you’ve achieved the clean, safe water your home deserves.
